- Thyroid
- Exploring the Association between Thyroid Function and Frailty: Insights from Representative Korean Data
-
Youn-Ju Lee, Min-Hee Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Jung-Min Lee, Sang Ah Chang, Jeongmin Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):729-738. Published online November 2, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1769
-
-
1,138
View
-
73
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
1
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
This study investigates the association between thyroid function and frailty in the old patients using representative data.
Methods
The study was conducted using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey conducted from 2013 to 2015. The study population included 2,416 participants aged 50 years and older with available thyroid function test data. Frailty assessment was performed using the Fried frailty phenotype. The prevalence of frailty was analyzed across different thyroid diseases and thyroid function parameters.
Results
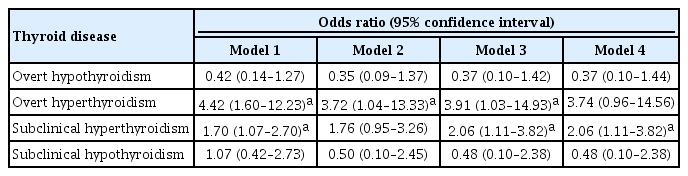
The significant association between thyroid dysfunction and frailty was observed in overt hyperthyroidism and subclinical hyperthyroidism. After adjusting for various factors, the association between thyroid dysfunction and frailty remained significant. On the other hand, overt hypothyroidism did not show a significant association with frailty in the adjusted analysis. For individuals with overt hyperthyroidism and subclinical hyperthyroidism, higher levels of free thyroxine (FT4) were significantly associated with an increased risk of frailty (aOR >999; 95% CI, >999 to 999). Among individuals with overt hypothyroidism, lower level of FT4 levels and high thyrotropin (TSH) levels showed a significant association with frailty risk (FT4: aOR, <0.01; TSH: aOR, 999). In participants with subclinical hypothyroidism, there were no significant associations between parameters for thyroid and frailty risk.
Conclusion
These findings suggest that thyroid dysfunction, particularly overt hyperthyroidism and subclinical hyperthyroidism, may be associated with an increased risk of frailty in the old patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Associations of thyroid feedback quantile-based index with diabetes in euthyroid adults in the United States and China
Heng Wan, Genfeng Yu, Yajun He, Siyang Liu, Xingying Chen, Yuqi Jiang, Hualin Duan, Xu Lin, Lan Liu, Jie Shen
Annals of Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- A Case of Sporadic Medullary Thyroid Cancer with RET G691S Polymorphism.
-
Min Kyu Kang, Jung Min Lee, Ji Hyun Kim, Min Young Lee, Ji Hyun Kim, Sung Dae Moon, Je Ho Han, Sang Ah Chang
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2009;24(4):293-297. Published online December 1, 2009
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2009.24.4.293
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Sporadic medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) is the most common form of MTC and somatic RET proto-oncogene mutations account for approximately 25% of the patients with sporadic MTC. However, other pathogeneses of sporadic MTC are still unclear. Not only RET mutation, but also polymorphisms of RET may have an association with sporadic MTC. We herein describe the association of MTC and RET proto-oncogene polymorphism. A 51-year-old man was diagnosed with MTC, which was incidentally found on a thyroid sonogram. The patient underwent total thyroidectomy and genetic mutational analysis of the RET gene. Genetic testing detected a polymorphism in codon 691 (G691S) on exon 11 of the RET proto-oncogene. His son and daughter had the same polymorphism. We report on this case along with a review of the related literature on RET gene polymorphism of sporadic MTC.
- Primary Hypogonadism Associated with Ankylosing Spondylitis.
-
Byoung Yeon Jun, Guk Jin Lee, Ji Hyun Kim, Jung Min Lee, Sang Ah Chang
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2008;23(5):352-357. Published online October 1, 2008
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2008.23.5.352
-
-
1,817
View
-
24
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Male patients with hypogonadism have an increased risk of developing rheumatic diseases. Most causes of hypogonadism related with rheumatic disease are karyotype abnormality such as Klinefelter's syndrome or Turner's syndrome and gonadal dysgenesis. A 24-year-old year male was admitted for pain of both hip joints that had worsened over 2 months. He had hip joint involvement from ankylosing spondylitis and did not show secondary sex characteristics. His sex hormones and gonadotropins levels indicated hypergonadotropic hypogonadism. The karyotype was 46 XY, and there was no obvious cause of hypogonadism. Here we report on clinical features of this first Korean case of primary hypogonadism accompanying ankylosing spondylitis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Ankylosing spondylitis associated with balanced reciprocal X-1 translocation
Young Hoon Kim, Jung Ouk Lee
Yeungnam University Journal of Medicine.2017; 34(1): 80. CrossRef - A Case of Klinefelter's Syndrome Accompanying with Polymyositis
Min Kyu Lee, Byung Sik Kim, Suk Hyun Jung, Gun Hwa Lee, Jin Ok Kim, Dong Hwi Rim, Yu Hwa Lee, Woong Jun Kim, So-Young Bang, Hye-Soon Lee
Journal of Rheumatic Diseases.2012; 19(3): 152. CrossRef
- A Case of Familial Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia with MEN1 Gene Mutation.
-
Hye Young Sung, Yeon Joo Chun, Hyeug Lee, Bum Jun Kwon, Kun Woo Park, Jung Min Lee, Sung Dae Moon, Sang Ah Chang, Je Ho Han
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(6):560-566. Published online December 1, 2006
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.6.560
-
-
1,826
View
-
27
Download
-
3
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN 1) is an autosomal dominant disorder that's characterized by the combined occurrence of primary hyperparathyroidism, endocrine pancreatic tumors and anterior pituitary adenomas, but such manifestations as carcinoid tumors, adrenal adenoma and lipoma are also seen. We report here on a case of a 52-years old man with MEN type 1. He had a parathyroid adenoma, empty sella and a non-functioning pancreatic and adrenal mass. On the genetic analysis, he was proven to have a mutation in the MEN1 gene (exon 2, 200-201, INS AGCCC). On the family study for the mutation, one of his siblings and his son proved to have the same mutation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Genetic and Epigenetic Analysis in Korean Patients with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1
Yoon Jung Chung, Sena Hwang, Jong Ju Jeong, Sun Yong Song, Se Hoon Kim, Yumie Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(3): 270. CrossRef - Endocrine Diseases in Diabetes Mellitus
Yongsoo Park
Hanyang Medical Reviews.2012; 32(4): 171. CrossRef - Somatic Mutational Analysis of MEN1 and Phenotypic Correlation in Sporadic Parathyroid Tumors
Young Su Chae, Hee Jin Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Myung-Chul Chang
Journal of the Korean Surgical Society.2009; 76(1): 15. CrossRef
|